Converting MKV to MP4 is one of the most common tasks for anyone working with video files today. Whether you are a beginner trying to play a video on a mobile device, a content creator preparing videos for YouTube or TikTok, or a professional editor optimizing storage and compatibility, understanding how to convert MKV to MP4 quickly and accurately can solve many playback and workflow issues. This guide covers everything you need to know — from basic definitions to advanced conversion settings, step‑by‑step instructions for multiple tools, best practices to maintain quality, troubleshooting common problems, and even batch processing workflows.
What Is an MKV File and Why Convert It
MKV stands for Matroska Video. It is a flexible container format that can hold multiple video, audio, subtitle, and metadata streams in one file. MKV is popular because it supports high quality, multiple audio tracks, advanced subtitles, and complex features. However, MKV is not supported by all devices and platforms. Many mobile phones, tablets, smart TVs, and web players prefer MP4 due to its universal compatibility and efficient performance.
MP4 (MPEG‑4 Part 14) is the most widely accepted video container worldwide. It supports a range of codecs and offers excellent compatibility with players, editors, and online platforms. Converting MKV to MP4 ensures that your videos play smoothly everywhere without additional codec installations or player issues.
Core Differences Between MKV and MP4
Understanding why you might want to convert between MKV and MP4 starts with knowing the technical differences:
MKV and MP4 are both containers, not codecs. A container holds video and audio data encoded in codecs like H.264, H.265, AAC, or MP3. An MKV file can contain multiple audio tracks, advanced subtitle formats like ASS or SSA, and metadata tags. MP4 is more standardized with broad support for H.264 video and AAC audio.
MKV offers flexibility and features that MP4 does not natively support, such as embedded chapters, rich subtitles, and multiple audio streams. MP4 sacrifices some of these capabilities in favor of universal compatibility. When you convert, you often remux (copy streams from one container to another) if codecs are compatible, or re‑encode if necessary.
When to Remux vs When to Re‑encode
The difference between remuxing and re‑encoding is critical for quality Convert MKV to MP4:
Remuxing means copying the video and audio streams from MKV into an MP4 container without altering the content. This method is fast and preserves original quality because it does not involve recompression.
Re‑encoding means decoding the original video and then encoding it again into a new format or settings. This can change resolution, bitrate, or codec, and can result in quality loss if settings are not chosen carefully. Re‑encoding is necessary when the source codecs are not compatible with the target container or device requirements.
Basic Tools You Can Use to Convert MKV to MP4
There are many tools available — online converters, desktop software, command‑line utilities, and mobile apps. Each has benefits and limitations. Here is a breakdown to help you choose:
Online Tools are convenient, require no installation, and work from any device with a browser. They are ideal for small files and quick conversions but often impose size limits and require good internet speed.
Desktop Tools offer more power, customization, and the ability to handle large files or batch conversions. Examples include VLC Media Player, HandBrake, FFmpeg, and dedicated converters.
Mobile Apps exist for Android and iOS, allowing you to convert videos directly on your phone or tablet. These are useful on the go but may have performance or battery limitations.
Convert MKV to MP4 Using an Online Converter
Online converters are perfect for quick tasks. Sites like CloudConvert, Zamzar, and Convertio support drag‑and‑drop uploads, instant conversion, and MP4 output options. Steps are generally similar:
Open the converter in your browser, upload or drag the MKV file, choose MP4 as the output format, adjust settings if available (such as resolution, bitrate, or codec), start conversion, and download the resulting MP4 file.
While convenient, online tools may struggle with large files or complex streams, and you should consider privacy and upload security if files contain sensitive content.
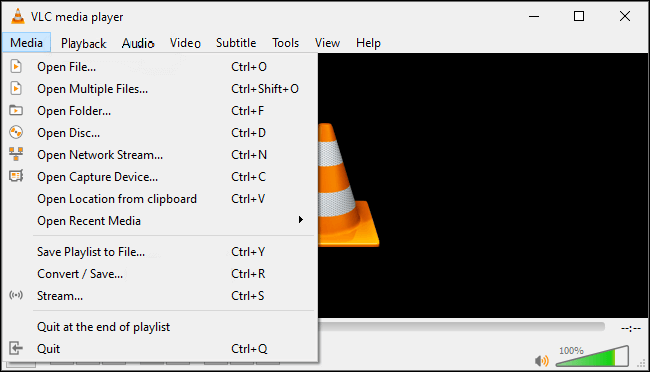
Convert MKV to MP4 Using VLC Media Player
Convert MKV to MP4, open‑source, and available on most operating systems. It is a popular choice for conversion because most people already have it installed.
To convert:
Open VLC and go to the Media menu.
Select “Convert / Save” and add your MKV file.
Choose “Convert” and pick MP4 as the destination format.
Set profile settings if needed, such as video codec H.264 and audio codec AAC.
Choose the output file location and start conversion.
VLC can sometimes struggle with advanced subtitle formats or multiple audio tracks. It may also require adjustments to settings to preserve quality.
Convert MKV to MP4 Using HandBrake
HandBrake is another free tool focused on video Convert MKV to MP4 transcoding with powerful options.
Install and launch HandBrake.
Load your MKV file.
Select an MP4 container, choose presets based on your target device or resolution.
Adjust video and audio settings, such as codec, bitrate, frame rate, and filters.
Start the encoding process.
HandBrake excels at quality optimization and device‑specific presets but does involve more settings and choices than basic converters.
Convert MKV to MP4 Using FFmpeg
FFmpeg is a command‑line tool that offers maximum control over conversion. It is ideal for advanced users who need precision and scripting capabilities.
To remux without re‑encoding:
Use a command like:
ffmpeg ‑i input.mkv ‑codec copy output.mp4
To re‑encode with specific settings:
Use commands specifying video and audio codecs, bitrate, resolution, and filters.
FFmpeg supports automation and batch processing, making it a powerful choice for professionals. However, it requires familiarity with command syntax.
Adjusting Video Quality and Settings
When converting, you often need to balance file size and quality. Key settings include:
Video Codec: H.264 is widely compatible and efficient. Convert MKV to MP4 offers better compression but may not play on older devices.
Bitrate: Higher bitrates mean better quality but larger files. Consider target device and platform requirements.
Resolution: Source resolution may be maintained or scaled down for smaller screens or faster playback.
Frame Rate: Preserve source frame rate unless specific needs demand conversion.
Audio Codec: AAC is standard for MP4, balancing compatibility and quality.
When converting for specific platforms like social media, choose settings optimized for those platforms’ recommended formats to ensure best performance and user experience.
Maintain Subtitles and Multiple Audio Tracks
MKV often contains subtitles and multiple audio streams. When converting to MP4, not all tools preserve these by default.
For subtitles:
Check if your converter supports subtitle extraction or burn‑in options.
Some tools only convert subtitles to hard‑coded format (embedded permanently in the video), while others allow soft subtitles in MP4.
For multiple audio tracks:
Advanced tools like Convert MKV to MP4 and some desktop converters let you select which audio streams to include. Otherwise, converters might default to the first audio track.
Understanding how to handle subtitles and audio streams ensures that multilingual content and accessibility features remain intact after conversion.
Common Problems and How to Fix Them
During conversion, you may encounter issues:
Video has no audio in the output file.
Check audio codec settings and ensure the converter supports the original audio format. Tools like FFmpeg can specifically map audio streams to the output.
Output video won’t play on a device.
Ensure that the target device supports the codec combination used. Older devices may require H.264 video and AAC audio.
Conversion fails or stops.
Large file uploads to online converters may time out. Use a desktop tool for reliable large file handling.
Quality loss after conversion.
Check if the tool is re‑encoding at low bitrate. Adjust settings to higher bitrate or use remuxing if possible.
By understanding typical issues and solutions, you can troubleshoot effectively without repeated failed conversions.
Batch Conversions for Multiple Files
When managing many MKV files, batch processing saves time. VLC and FFmpeg scripts can process entire folders automatically.
Using FFmpeg for batch:
Write a simple script to iterate over all MKV files and convert to MP4 format using remux or re‑encode commands. This is highly efficient for large collections or archival purposes.
Batch converters with GUI also exist in some desktop software, letting you queue files and set global settings.
Choose the Right Tool for Your Needs
Selecting the best tool depends on:
File size and number of files.
Level of customization needed.
Device compatibility.
Speed vs quality priorities.
Online tools are fast for small files, VLC and HandBrake are great for general conversions, and FFmpeg is ideal for advanced or automated workflows.
Best Practices for Video Conversion Projects
Before converting:
Back up original files.
Know your target devices.
Test settings with a short clip before batch processing.
Maintain codec compatibility to avoid errors.
After conversion:
Verify playback on intended devices.
Check subtitles and audio track accuracy.
Compare quality to source before deleting originals.
Following these practices ensures that your videos remain accessible and in the best possible quality.
Advanced Techniques and Optimization Tips
If you want to go beyond basic conversion, explore:
Two‑pass encoding for optimal quality and bitrate.
Adaptive bitrate settings for streaming use.
Using hardware acceleration (like GPU‑based encoding) for faster processing.
Custom profiles in tools like HandBrake to save preferred settings.
Understanding these can significantly improve workflow efficiency and output quality for advanced projects.
Mobile Conversion Workflows
Mobile apps exist that let you convert MKV to MP4 directly on your phone. While performance may vary and larger files can strain devices, lightweight tools are useful when desktop access isn’t available.
Choose apps with clear settings and preview functions. Always monitor storage and battery usage.
Security and Privacy Considerations
When using online converters, be cautious:
Avoid uploading sensitive or private videos to public sites.
Check privacy policies to ensure files are deleted after conversion.
Use HTTPS connections and reputable services.
For maximum privacy, use desktop or local tools so files never leave your device.
Comparison: Popular Tools at a Glance
A quick comparison helps decide:
Online Tools: Easy but limited size and settings.
VLC: Reliable and free, moderate options.
HandBrake: Powerful presets and quality control.
FFmpeg: Most flexible and scriptable.
Each tool has strengths, and the best choice depends on your specific project goals.
Real‑World Use Cases
Content creators preparing videos for platforms like YouTube, Instagram Reels, or TikTok often need MP4 at specific resolutions and aspect ratios. Understanding conversion tools allows them to optimize audience engagement.
Archivists preserving video collections may convert to MP4 for compatibility with media servers like Plex or devices like smart TVs.
Educators and trainers sharing tutorials benefit from universal MP4 compatibility with learning platforms.
Future of Video Formats
As codecs evolve and devices support newer formats like AV1, conversion workflows may adapt. However, MP4 remains the most universal format today, making conversion skills continuously relevant.
Keeping up with codec developments ensures compatibility and efficiency for video professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the fastest way to convert MKV to MP4? Remuxing with FFmpeg or using a fast desktop converter offers quick results without quality loss.
Can I convert without losing quality? Yes, remuxing preserves original streams. Re‑encoding can cause quality changes, so use high bitrate or efficient codecs.
Will subtitles always be preserved? Not always. Check converter support for subtitle formats, and choose tools that let you include or adjust subtitle handling.
Which converter is best for beginners? VLC and online converters are easiest for beginners.
How do I batch convert many files? Use FFmpeg scripts or desktop software with batch queue functions.
Conclusion
Converting MKV to MP4 doesn’t have to be confusing. With the right understanding of containers, codecs, and tools, you can achieve high‑quality results tailored to your needs. From basic online converters to advanced command‑line workflows, this guide equips you with everything necessary to convert efficiently and effectively — ensuring compatibility, quality, and control over your video content.
By applying the methods, tips, and insights in this guide, you can confidently convert MKV files to MP4, troubleshoot issues, and optimize for any device or platform without sacrificing quality or efficiency.